Why hemp protein?
Hemp protein consists of more than 65% globular edistin, which is the most easily digestible form of protein in nature and is only found in seeds from fiber hemp.
Hemp protein shows a number of health benefits including:
- Strengthens the immune system
- Increases energy
- Exhibits anti-inflammatory properties
- Beneficial effect on digestion
- Improves muscle regeneration
- Increases muscle mass
- Regulates cholesterol levels
- Reduces the risk of osteoporosis
- Accelerates metabolism
- Influences a longer feeling of satiety
Benefits of hemp protein:
- Non-allergenic
- Gluten-free
- Lactose free
- No added sugar
- No thickeners
- No preservatives or colorants
- Rich source of fiber
- Complete amino acid composition
- Vegan formulation
- Hemp protein has a high concentration of BCAAs
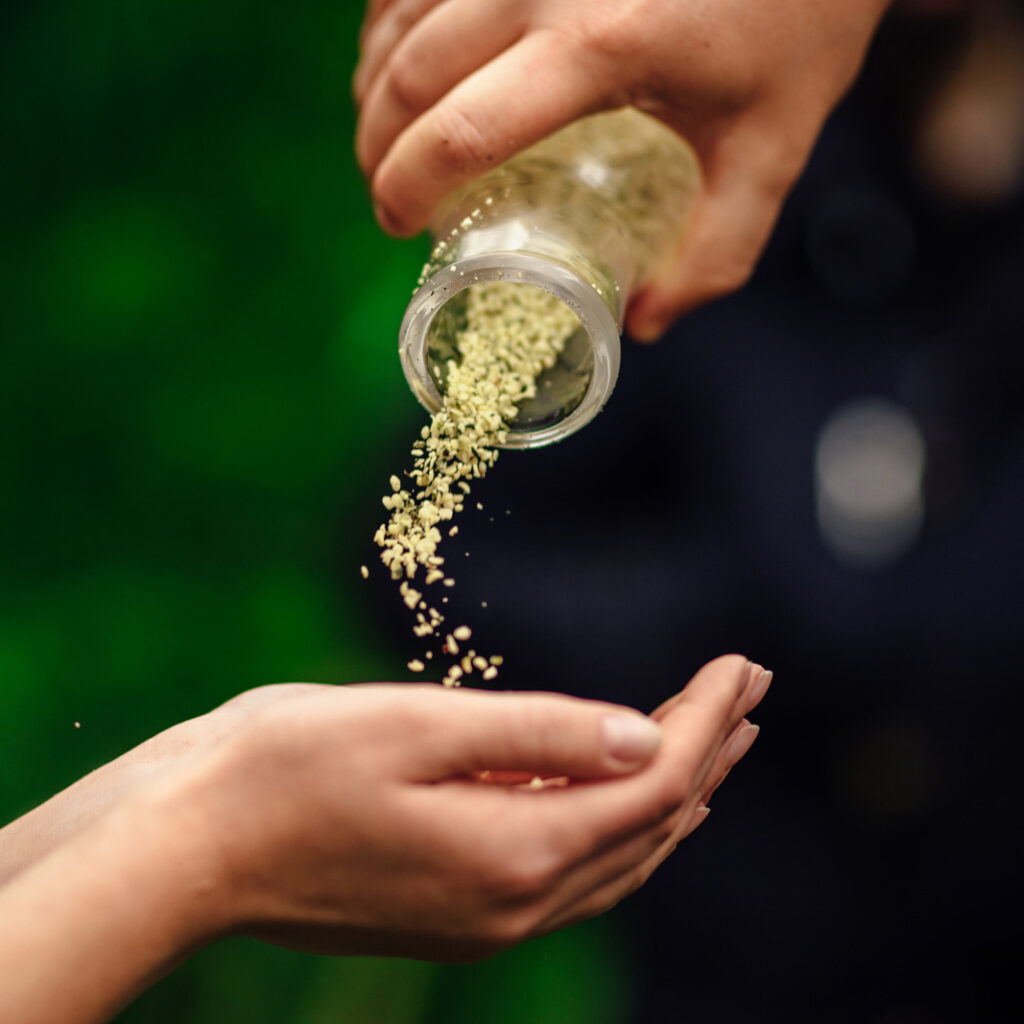

Cannabis seed
Multi-crop plants
Seed/fiber hemp (Cannabis sativa L. var sativa) is a multi-crop plant with a number of applications in various industries: food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, chemical, textile, pulp and paper, veterinary, feed, beekeeping, insulation or energy.
From our perspective, hemp seeds are an excellent source of protein and nutrients.
Environmental protection
Fiber hemp and the environment
The cultivation of fiber hemp shows a very positive impact on the quality of the environment.
Clean the soil of harmful substances
Reduce weed
growth
Improve fertile
soils

Pollen-based crop isolation

Crops do not need to be fertilized with pesticides

Neutralize CO2:
1ha up to 25 t/year

They are a benefit
for bees
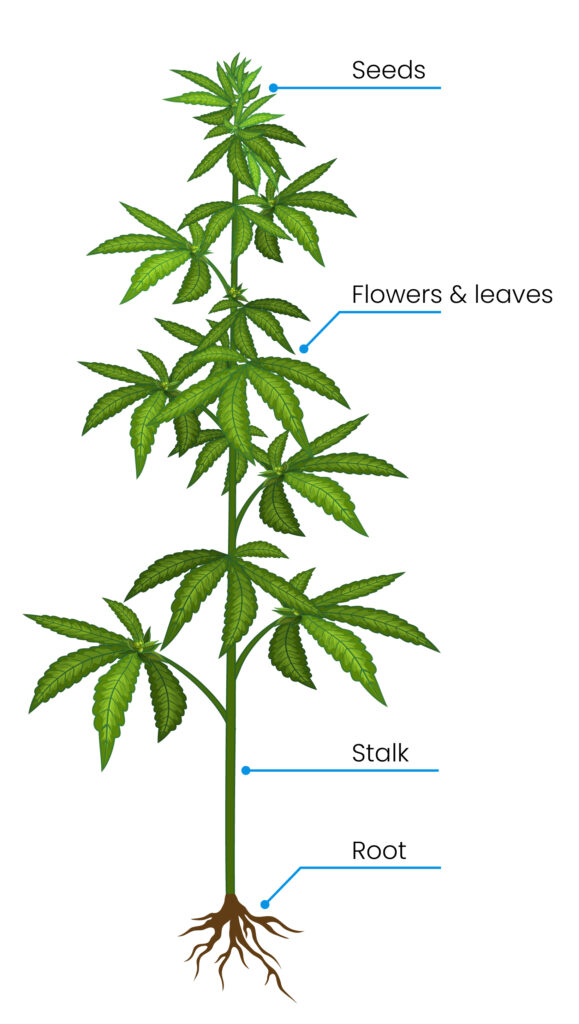
industrial application
Cannabis sativa
Seeds
Foods
- Protein (isolates, concentrates)
- Cooking oils
- Fiber and hemp flour
- Animal feeds and feed additives
Industrial products
- Oil paints
- Varnishes and lubricants
- Fuels
Personal hygiene articles
- Soaps and shower gels
- Shampoos and conditioners
- Creams and lotions
- Organic cosmetics
flowers and leaves
- Medicines
- Medical devices – patches and ointments
- Dietary supplements
- Cosmetics
- Foods
- Aromatic and flavor substances
Stalk
Industrial textiles
- Yarns
- Ropes and cords
- Nets
- Tarps
- Carpets
- Clutch and brake linings
Building materials
- Hemp bricks
- Building insulations
- Building boards
- Acoustic curtains
- Reinforced composites
- Packings and sealants
Materials substitutes
- Wood (furnitures)
- Bioplastics (bottles, packaging, toys)
- Composites (automotive)
- Paper
Root
Medicinal properties
- Inflammatory
- Painful conditions
- Fever
- Acne
- Migraine
- Abrasions
- Dysentery
- Skin swellings
comparison
Legumes vs. fiber hemp
Hemp seed shows an advantage over legumes, both in the food and organic areas:
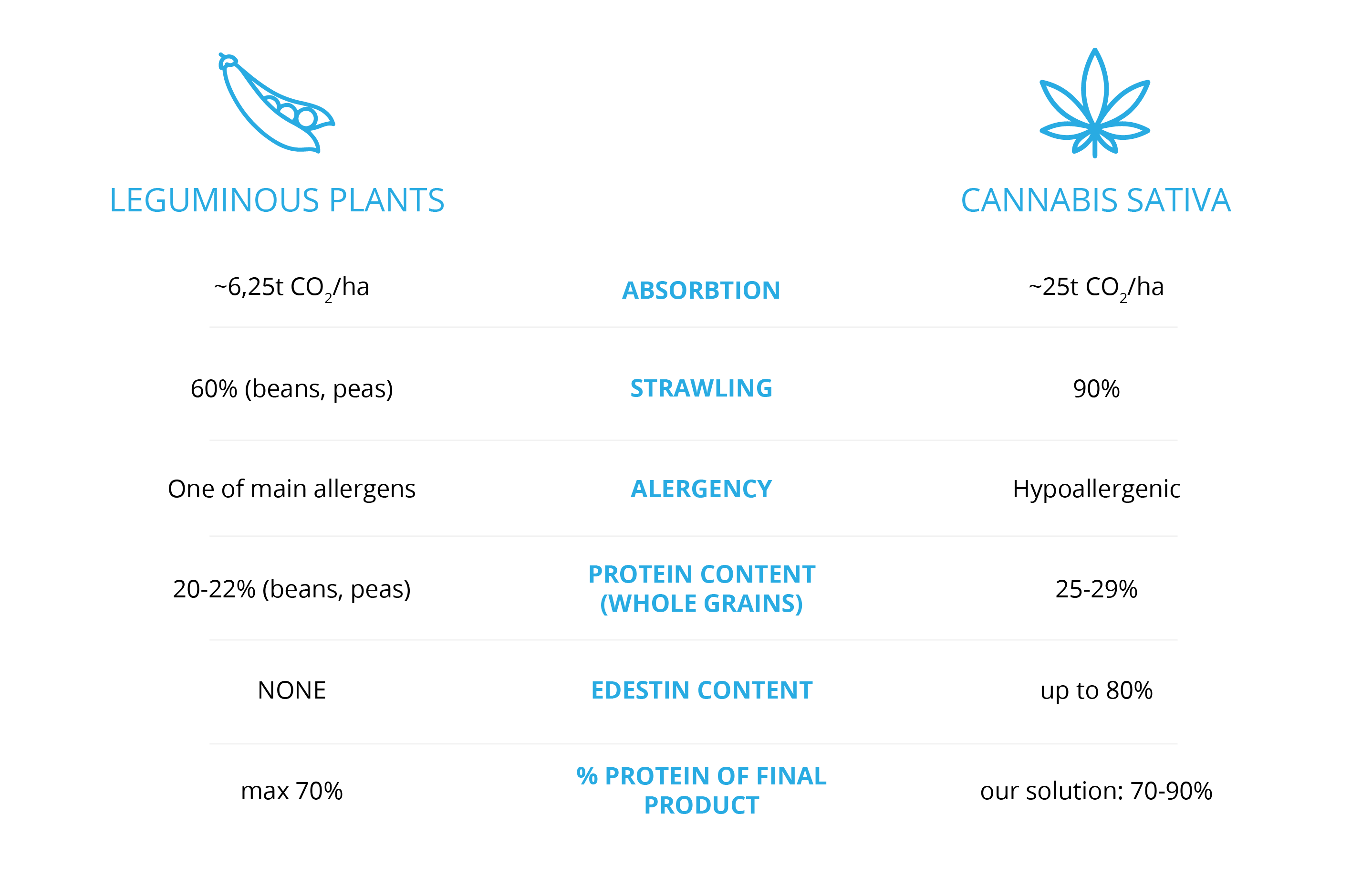
More information
Hemp protein:
- Is rich in natural antioxidants and bioactive compounds such as phenolic acids, tocopherols, carotenoids, phytosterols.
- Contains all essential amino acids that must be supplied to the human body including the highest content of glutamic acid about 3.74-4.58% and arginine 2.28 – 3.10%. [1]
- In contrast to soy protein and casein on the plus side in hemp protein is the content of sulfur amino acids whose concentration here is the highest. [1]
- The ratio of essential amino acids to total amino acids was much higher than in soy protein and comparable to casein. [1]
- Hemp seed turns out to be a very protein-rich source, containing a protein content (20-25% some sources even indicate up to 30%) higher or comparable to other protein-rich products such as quinoa (13%) [2] , chia seeds (18.2-19.7%)[3], buckwheat seeds (27.8%) and flax seeds (20,9%) [2].
- Hemp protein is highly digestible, has a good profile of essential amino acids (required, among others, for infants similarly to casein except for lysine but this is a limitation only for infants and children under 5 years of age who require higher proportions of lysine, but you can always enrich). [1]
- Benefits are also obtained given the content of amino acids such as arginine, which is a precursor for the formation of nitric oxide (NO) which is important for the protection of the cardiovascular system. It also acts on immune system function and muscle regeneration [3], and hemp protein is a good source of well-absorbed arginine.
- The sources of amino acids in hemp protein are albumin and edestin. These are easily digestible, non-allergenic proteins and are an advantage over soy protein, which can be a source of sensitization. [1].
- The advantage of hemp protein is the absence of genetically modified crops, as is the case with soybeans hemp seeds according to EFA references [3] are an excellent natural source of elements such as potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, iron, copper , zinc and manganese. In turn, the content of toxic compounds such as cadmium is lower than the upper limit recommended by FAO/WHO [4].
- Antioxidant in the highest concentrations is tocopherol gamma isoform in addition we have compounds from the flavonoid group such as flavanones, flavonols, flavanols and isoflavones where the most important representatives are naringenin, epicatechin, kemferol glycosides and daidzein [5].
- Also present are lignans, which are biogenetically derived compounds through the transformation of chiacid. [6] Lignans were isolated and identified from hemp seeds with high protective potential against LDL oxidation: cannabisin A [7] cannabisin F and grossamide [8] . From the point of view of this action, n-trans caffeoyl tyramine is also an important compound.
- Hydrolysis of hemp proteins leads to hydrolysates with high biological activity characterized by antioxidant activity [9], hypotensive [10], antiproliferative [11] , hypocholesterolemic [12], anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective [13], [14].